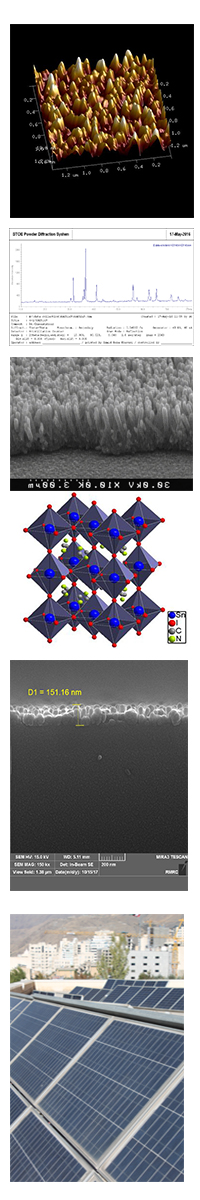
- Morteza
- بازدید: 375
Synthesis of push–pull porphyrin dyes with dimethylaminonaphthalene electron-donating groups and their application to dye-sensitized solar cells
Maryam AdinehPooya TahayWei-Kai HuangHui-Ping WuEric Wei-Guang DiauNasser Safari
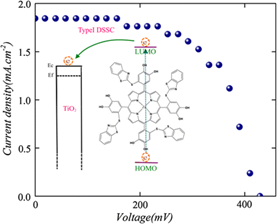
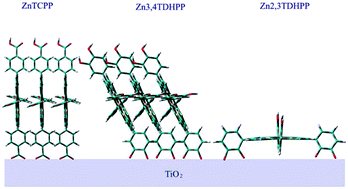
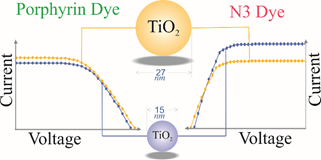
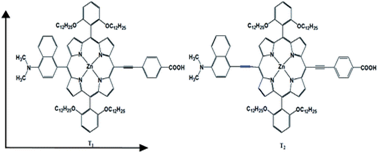
Two new donor–π-bridge–acceptor zinc porphyrins with dimethylaminonaphthalene electron donating moieties, coded T1 and T2, were synthesized and used as sensitizers in dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). Both dyes showed excellent photovoltaic properties with power conversion efficiencies of 8.0 and 9.6% for T1 and T2 respectively, for which the device performance of T2 dye is superior to that of N719 dye.
Link: http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlelanding/2016/ra/c6ra23882c/unauth#!divAbstract